Content is the backbone of any website. It helps search engines understand what your site is about and rank it accordingly. The more quality content you have, the higher your site will rank, leading to more traffic, more service inquiries, more sales, phone calls, or any other conversions that ultimately bring money to your business.
However, not everyone knows what quality content means in mid-2024. For many, good content is something that simply appeals to someone, like their grandma.😁
Many website owners, who are experts in their field, try their hand at writing content for their website. They think their content is high quality because they know their subject matter inside and out. However, in practice, this content often remains invisible to readers because it isn’t optimized. Someone might feel a burst of inspiration, a thought they believe is illuminating and must be shared on their website. But without proper optimization, even the best ideas can go unnoticed.
All of this is great, and no one is stopping you from creating, writing, and considering your work a masterpiece. But we’re talking about high-quality content for a website – content that quickly reaches the top of search engine results, gets read, and converts readers into customers. The more readers we convert, the better the content is considered. Even if your grandma doesn’t like the content, it doesn’t matter. If the content brings in huge targeted traffic and revenue – it’s quality content.
So, what is high quality content? Quality content ranks highly in search engines, brings targeted traffic, and has a high conversion rate – when users read the content and take action, such as ordering a product or service, making a phone call, etc.
If your idea of quality content is different, you might want to consider writing books, where success comes from contracts with publishers rather than search engine rankings. Today, we’re focusing on content for websites.
Types of content on a website
A website typically contains various types of content, each with specific purposes and requirements. Here are three primary types:
- For general pages: About Us, Contact Us, Our Team, etc.
- For commercial pages: all pages whose purpose is to order a service/product.
- For blog.
Content for general pages essentially represents the brand. These pages don’t require intensive optimization but should effectively communicate your brand’s story and achievements. Highlight your brand’s credibility by mentioning accolades or sharing the story of how your ancestors founded the business at the dawn of Canada’s history.⚡However, it’s important to back up these claims with evidence like certificates, Google reviews, video testimonials. If your brand is relatively new, it’s acceptable to enhance your achievements slightly – just avoid going overboard.
Commercial pages need what’s called SEO content. For example, imagine we have a page for dental services in a specific city. By following certain rules, you can achieve high-quality content that ranks well in search engines. Users land on these pages to make a conversion (in this case, to engaging your dental services).
On commercial pages, Google wants to see a comprehensive description of the service or product. Of course you need to use keywords here. In the past, keywords were inserted left and right, but now you have to pay attention and don’t spam, don’t overuse keywords. Texts literally looked too agressive – buy this, order that. All this is long gone and can lead to dire consequences for the site. Even if services that check for spam show you that everything is fine, but you managed to insert 50 keywords in a small article, nothing good will come out of it. Google has long ago learned to see this nonsense and will not rank highly such content.
Gradually, the importance of keywords in content began to lose its power. Now in 2024, the role of keywords in the body of the article has decreased significantly. Don’t get me wrong they still need to be used, but only in the title, subheadings and literally a few times (up to 5) in the main text.
It seems straightforward to have website pages that describe the brand and commercial pages for ordering services or products, so why bother with a blog? Many sites neglect blogging, and that’s a big mistake. A blog is a true treasure for the website.
Let’s take another example – an online store selling TVs. If you gather queries related to buying a TV, you’ll find there aren’t that many, but the competition is incredibly high. Ranking well for these commercial queries requires significant time and money invested in SEO.
A blog serves as a sort of workaround. The content doesn’t directly sell TVs but implies it. Competition for blog topics is much lower, and the range of possible subjects is practically limitless. This kind of content can easily reach the top of search engine results and eventually convert into sales.
Moreover, a blog is an ideal place for internal linking within the site, which is one of the most important ranking factors.
The 5 steps to creating high quality content for a blog
Creating perfect quality content for a blog consists of the following 5 steps:
- Finding keywords.
- Writing content following the E-E-A-T guidelines.
- Creating images.
- Checking for uniqueness and spam.
- Optimization of meta tags, titles, images, linking.
Keyword research. This is a vast topic and there is a tremendous amount of information written about it. Experience is crucial here, because knowing about it and to do it are two different things.
Let’s start with the basics: it all depends on the keywords. For a blog, you should choose informational keywords that imply conversion without explicitly stating it. For example, Effortless Marketing provides SEO services in Calgary, but this article is about content, not directly promoting SEO services. I know that readers of this article are looking for quality content for their websites. These readers may include copywriters, SEO specialists, and of course, website owners who need that content. Some of them will use the knowledge they’ve gained to write their own content, while others will likely turn to Effortless Marketing for help.
You can research keywords using a variety of web services. I recommend using Semrush as your primary tool and Google Keyword Planner as an add-on.
When searching for keywords, it’s crucial to choose ones that show a reasonable number of queries per month (I recommend 20 or more). Many people mistake ordinary phrases that arise in their minds for effective keywords.
Let’s imagine you provide yoga services and decide to write an article about a specific pose that’s a miracle cure for back pain. Only you and a few monks in Tibet know about this pose. Even if it grants immortality, it will remain invisible on the internet if there’s no demand for it.
It’s important to note that very popular sites or authors with impeccable authority don’t need to worry about keywords and demand. These authors create demand themselves. Their sites attract hundreds of thousands of users daily, eagerly awaiting any word from them. Even if they just write “Quack,”😂 it will be read by many people.
However, if you’re not a celebrity, your words don’t have that authority, and your site doesn’t have huge traffic, keyword research is essential.
Effective keyword research ensures that the content you create will be seen and read by the right audience. Without it, even the best content can go unnoticed.
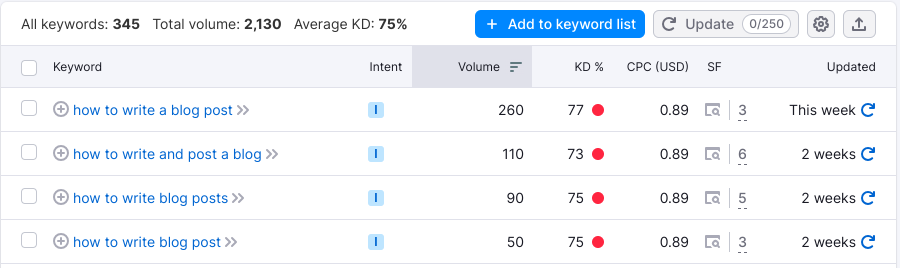
I want to discuss competition and how to find keywords that can help your article quickly rise to the top of search engines. One key concept is the “long tail” keyword, which refers to longer, more specific phrases. Even informational queries can have high competition. For example:
We can see that each keyword has a lot of searches, and the Keyword Difficulty (KD) is very high. KD is measured from 1 to 100 – the higher the number, the harder it is to rank well quickly without additional efforts like link building.
I’ve mentioned that the demand for keywords should be at least 20 queries per month for each keyword, but you don’t need to aim much higher. Of course, it could be 30, 40, or 50, but keep in mind that the more queries a keyword has, the higher the competition.
I also recommend measuring competition manually rather than relying solely on indicators like KD (Keyword Difficulty). To manually check a keyword’s competition, paste it into a Google search and see how many sites have a direct occurrence of the keyword in their title tag. For example, suppose you find the keyword “how to care for blue hedgehogs” and there is demand for it. When you search this keyword on Google, if you don’t find any sites with this exact phrase in their titles or any relevant information about blue hedgehogs, you’ve struck gold.
Of course, this is humorous, and no blue hedgehogs exist (although I’m not entirely sure😂), but ideally, you should strive to find keywords that users are searching for and that no one has yet answered, or very few have addressed. This strategy helps you create unique content that fills a gap in the market, increasing your chances of ranking well and attracting traffic.
If you manually check the keyword “how to write a blog post,” you’ll find that direct or near-direct matches appear on almost every site up to page 5 (figuratively speaking; I didn’t actually check). Do you think writing an article with the same keyword will get you to the top of search engines? No!
Understanding this step is crucial; otherwise, everything else won’t make sense. If all of this feels like a dark forest, you know what to do🙂 -ask us– digital marketing agency Calgary.
E-E-A-T compliant content writing. The era of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) has arrived, when search engines began to pay special attention to the author’s experience in the field, who writes the content, what evidence there is about the written content, and where the content is posted. These principles essentially nullify the concept of copywriting. That is, Google does not want articles to be written by faceless authors who do not understand what they are writing about, but only quickly read a few sources and then paraphrase achieving good unique content.
Let’s take this article as an example. It shows my authorship, which is a good start because many blog articles don’t even have that. Authorship should be labeled appropriately, using standards like Schema markup. The latest version of the WordPress plugin All in One SEO (AIOSEO) can mark the author as needed.
By providing a link to my business profile, Google can see that I am writing on a topic where I have some authority. Through my publications and activity as an author, Google can analyze my expertise. While I may not be the top global SEO expert, referencing more authoritative experts adds value to my words.
Lastly, this article is posted on a corporate website with a good reputation and continuous development, which enhances the site’s trustworthiness. The higher these E-E-A-T indicators are, the more likely the article will rank highly in search engine results.
Creating a blog article today should ideally be done by a knowledgeable author, but finding such an author can be challenging and expensive. That’s why we use copywriting, but with a deeper focus. Instead of relying solely on copywriters, the process should now involve SEO specialists who can gather keywords, outline the structure, optimize meta tags, and work directly with representatives of the website being promoted. Here’s how this can look:
Let’s say we have a website for a lumber supplier. As an SEO specialist, I would research keywords, outline the structure, and ask the company owner to share some thoughts on the topic. It doesn’t have to be a full article – just some insights. The owner of the company, with years of experience, will have knowledge that neither the optimizer nor the internet can fully provide. These insights are invaluable and come directly from the owner’s expertise.
Next, we take these thoughts and expand them into a full-fledged article, perhaps using tools like ChatGPT. It’s crucial to indicate that the article’s author is the business owner. This approach combines the principles of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) with modern copywriting techniques.
If involving company representatives in the content creation process is not feasible, then classic copywriting is the fallback. This involves researching various sources, rewriting the content, and still attributing it to company representatives. While this may seem deceptive, it is a common practice and, importantly, it works.
I want to talk directly about writing an article. The days of stuffing an article with keywords and creating a ToR (Terms of Reference) longer than the article itself are over. What truly matters now is the value of the information. If we’re discussing the rules, we should focus on:
- Article Length: Aim for an average of 1,500 words or around 10,000 characters without spaces. More is fine, but less isn’t a big deal. While there are no strict rules, observations suggest that extremely long articles (around 4,000 words) are not ideal for Google, and very short articles (under 300 words) can’t adequately cover the topic, resulting in lower rankings.
- Readability: Use paragraphs, subheadings, lists, tables, images, color highlights to break up the text and make it more readable.
- Answering the Topic and Subheadings: You don’t need to be a top-notch writer to create high-quality content that ranks well. Just focus on answering the main question of the topic and providing some arguments. For example, if the topic is “What is better, BMW or Mercedes?”, you could write: “I prefer BMW over Mercedes. Once, a Mercedes ran over my foot, and since then, I’ve disliked them.” Simple and to the point.😂Humor aside, I want to reiterate – it doesn’t matter what kind of writer you are. If you are an expert in a certain field, any of your thoughts on the topic will be of value.
- Maximum description of the topic of the article in the first 100 words: it is necessary for the reader to immediately understand whether the article is suitable for him or not + Google bots also read it so pay special attention to this section.
- Use Internal Links: There are no clear rules on the exact number of internal links to use. Neil Patel, in his article “Step-by-Step Guide: Content Optimization,” emphasizes the importance of using lots of internal links naturally. Obviously, if you have a 100-word article with a link in every sentence, it’s overkill. While it’s hard to define “natural” link usage, here are some guidelines: for a standard 2,000-word article, use up to 5 internal links and up to 5 external links. When referring to external sources, you don’t need to worry about closing these links from passing “link juice” to them – those practices are outdated. Simply set external links to open in a new tab. The value you provide through external links will return to you in full.
Creating images. Every article should include pictures, photos, screenshots, infographics, animations, and similar visuals. These elements enhance the reader’s experience and break up the text.
However, it’s crucial that all visuals are unique and not taken from other people’s resources. Ideally, you should have a graphic designer and a photographer on hand to create these images. If you don’t have these specialists available, you can use ChatGPT to help generate ideas and create images, which are unique by default. Read in detail can I use AI images on my website?
Checking for uniqueness and spam. Writing a high-quality article already implies that it is created by a reputable author, drawing from their own knowledge and experience. Therefore, checking for uniqueness is typically unnecessary. However, if you use any external sources to assist in writing the article, it’s essential to verify its uniqueness. I recommend using 1Text.com for this purpose. Uniqueness should always be 100%.
Spam, in this context, refers to the frequency of keyword or random word usage. It’s important to monitor this parameter using the same service. Ensure that the spam score does not enter the red zone, as this is critical for maintaining the quality and readability of your content.
Optimization of meta tags, subheadings, images, and internal linking. Even high-quality content won’t rank highly without proper optimization. This is the job of an SEO specialist and is a separate topic on its own. Key meta tags such as <title>, <description>, and <alt> tags for images are the first things search engines pay attention to. These meta tags should include important keywords.
- Title: Should not exceed 70 characters and should contain important keywords. Make it attractive (consider using emojis) and logical.
- Description: Should be a maximum of 260 characters, also containing important keywords and crafted to be compelling.
- Alt Tags: Use for images to describe the content of the image, which helps with SEO and accessibility.
Keywords should also be used naturally in the title, subheadings, and a couple of times in the main text. Avoid keyword stuffing to ensure your content remains readable and engaging.
Conclusions
To summarize this article, quality content is created by two key people: an expert who understands the topic through experience, and an SEO optimizer who can properly set the topic and optimize the content for high ranking. One cannot work effectively without the other; content will not be considered high quality if either element is missing. Even if the content reveals the secrets of immortality, without proper optimization, it won’t be read. Conversely, knowing how to optimize content competently is pointless without expertise in the topic.
P.S.
This article was created by 1 person, me. I am both an SEO optimizer and a person who knows what he is writing about, 2 in 1… maybe I have bipolar disorder?👀